What is Machine Learning?
Machine learning teaches computers to do what comes naturally to
humans and animals: learn from experience. Machine learning algorithms use computational methods to “learn” information directly from data without relying on a predetermined equation as a model. The algorithms adaptively improve their performance as the number of samples available for learning increases.
Machine learning algorithms find natural patterns in data that generate insight and help you make better decisions and predictions. They are used every day to make critical decisions
in medical diagnosis, stock trading, energy load forecasting, and
more. Media sites rely on machine learning to sift through millions
of options to give you song or movie recommendations. Retailers
use it to gain insight into their customers’ purchasing behavior.
How Machine Learning Works
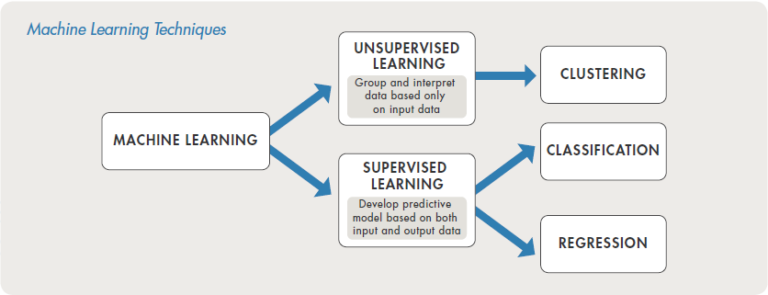
Machine learning uses two types of techniques: supervised learning, which trains a model on known input and output data so that it can predict future outputs, and unsupervised learning, which finds hidden patterns or intrinsic structures in input data.
Supervised Learning
The aim of supervised machine learning is to build a model that makes predictions based on evidence in the presence of uncertainty. A supervised learning algorithm takes a known set of input data and known responses to the data (output) and trains a model to generate reasonable predictions for the response to new data. Supervised learning uses classification and regression techniques to develop predictive models.
Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning finds hidden patterns or intrinsic structures
in data. It is used to draw inferences from data-sets consisting of
input data without labeled responses. Clustering is the most common unsupervised learning technique. It is used for exploratory data analysis to find hidden patterns or groupings in data. Applications for clustering include gene sequence analysis, market research, and object recognition.
How Do You Decide Which Algorithm to Use?
Choosing the right algorithm can seem overwhelming—there are dozens of supervised and unsupervised machine learning algorithms, and each takes a different approach to learning. There is no best method or one size fits all. Finding the right algorithm is partly just trial and error—even highly experienced data scientists can’t tell whether an algorithm will work without trying it out. But algorithm selection also depends on the size and type of data you’re working with, the insights you want to get from the data, and how those insights will be used.
When Should You Use Machine Learning?
Consider using machine learning when you have a complex task or
problem involving a large amount of data and lots of variables, but
no existing formula or equation. For example, machine learning is a
good option if you need to handle situations like these:
Real-World Examples
Creating Algorithms that Can Analyze Works of Art Researchers at the Art and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory at Rutgers University wanted to see whether a computer algorithm could classify paintings by style, genre, and artist as easily as a human. They began by identifying visual features for classifying a painting’s style. The algorithms they developed classified the styles of paintings in the database with 60% accuracy, outperforming typical non-expert humans. The researchers hypothesized that visual features useful for style classification (a supervised learning problem) could also be used to determine artistic influences (an unsupervised problem).
They used classification algorithms trained on Google images to identify specific objects. They tested the algorithms on more than 1,700 paintings from 66 different artists working over a span of 550 years. The algorithm readily identified connected works, including
the influence of Diego Velazquez’s “Portrait of Pope Innocent X” on Francis Bacon’s “Study After Velazquez’s Portrait of Pope Innocent X.”
Optimizing HVAC Energy Usage in Large Buildings
The heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning (HVAC) systems in office buildings, hospitals, and other large scale commercial buildings are often inefficient because they do not take into account changing weather patterns, variable energy costs, or the building’s thermal properties. Building IQ’s cloud-based software platform addresses this problem. The platform uses advanced algorithms
and machine learning methods to continuously process gigabytes of information from power meters, thermometers, and HVAC pressure sensors, as well as weather and energy cost. In particular, machine learning is used to segment data and determine the relative contributions of gas, electric, steam, and solar power to heating and cooling processes. The building IQ platform reduces HVAC energy consumption in large scale commercial buildings by 10% – 25% during normal operation.
Detecting Low-Speed Car Crashes
With more than 8 million members, the RAC is one of the UK’s largest motoring organizations, providing roadside assistance, insurance, and other services to private and business motorists.
To enable rapid response to roadside incidents, reduce crashes, and mitigate insurance costs, the RAC developed an on board crash sensing system that uses advanced machine learning algorithms to detect low speed collisions and distinguish these events from more
common driving events, such as driving over speed bumps or potholes. Independent tests showed the RAC system to be 92% accurate in detecting test crashes.