

Digitalization means the use of digital technologies and of data (digitized and natively digital) in order to create revenue, improve business, replace/transform business processes (not simply digitizing them) and create an environment for digital business, whereby digital information is at the core. It can change how products are designed, fabricated, used, and serviced, just as it’s transforming the operations, processes, and energy footprint of factories and supply chains.
Digitalization involves capturing analog signals and storing the results in digital form. This is usually done via sensors, which sense analog signals like light and sound, and transform them to their equivalent digital forms via an analog-to-digital converter chip or a whole circuit dedicated to converting a specific analog signal. This works by converting the continuous stream of signal or data found in most analog data types into discontinuous values.
Digitalization Solutions is implemented in Automotive Industry. There we are measuring TBM (Time Base Maintenance), CBM (Condition Base Maintenance), Machine Status, Stoppages and Alarms Data reading from existing machine and adding field sensors regarding CBM purpose.
Architecture:
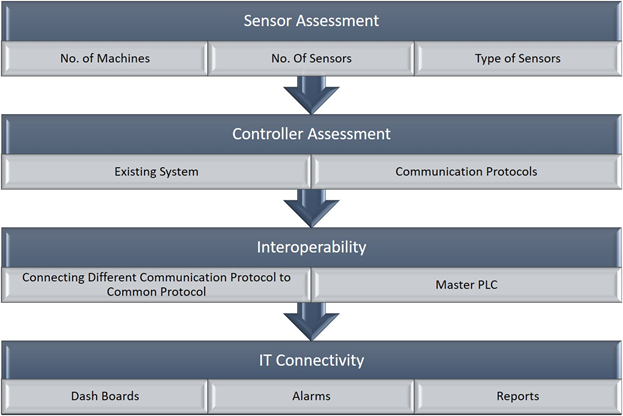
Based on the analysis and assessment, the process of digitization is shown blow:
Step 1: Sensor Assessment – Here the process of the plant is studied to find out the what are the parameters need to be monitor and control. Based on the parameters the sensors are selected like Temperature, pressure, flow, etc. And also, we will check the existing sensor and their conditions.
Step 2: Controller Assessment: In the survey we also check the existing systems, their communication protocols and their compatibility with new system. If the existing system is Obsolete system then we recommend to change it to new system for the compatibility and reliability.
Step 3: Interoperability: Interoperability is a characteristic of a product or system, whose interfaces are completely understood, to work with other products or systems, at present or in the future, without any restrictions. We can connect different make and model controller to master controller for the collection of Data.
Step 4: IT Connectivity: After collecting Data in Master Controller the Data is sent to the Server or Cloud. The communication between the Hardware and Software (Cloud/Server) is called IT Connectivity. Here the Master Controller is capable of network protocols like MQTT, SQL, FTP, HTTP, etc. The Data is sent through this network Protocol to MES Software or Server.

According to the Assessment the plant is divided into Zones and each zone consists of individual PLC to collect the Data. In each zone there is Scanner connected to each machine to collect the analog signal from the field and from the machine and it is communicated to Zone PLC through Modbus Communication. The Zone PLC then communicated to Master PLC through Modbus Communication and the Master is Connected to SCADA through OPC protocol. Here in SCADA all TBM, CBM, Machine Status, Stoppages and Alarms can be seen.

Sensor Details:
Each Machine we are implanting is having below sensors
Temperature Sensors: Used for measuring Motor Body Temperature, Oil in Hydraulics, etc.
Pressure Sensors: Hydraulic oil and Air Pressure purpose. Pressure Transmitter o/p signal is Analog this is connected to scanner.
Level Sensor: Level sensor is used to measure coolant tank level and Water level, etc.
Flow: It will measure the Flow of Liquid in Pipe, etc.,
Vibration Sensor: Motor Vibration purpose.
CT: Used for Motor Current purpose.

MES Software Features:
Time-based maintenance (TBM): Is maintenance performed on equipment based on a calendar schedule. This means that time is the maintenance trigger for this type of maintenance.
Condition-based maintenance (CBM): Is a maintenance strategy that monitors the actual condition of an asset to decide what maintenance needs to be done.
Machine Status: In this the user can get to know the machine parameters like its temperature, pressure and alarms, etc., Basically, the machine is working on the setpoints.
Stoppage: In this the user can get to know when the machine goes to breakdown and how much time it took to start the machine. The user also gets to know what is reason of Breakdown.
Alarms: If the machine is running above set points the alarms will be generated to notify the user to do a quick maintenance checkup to rectify the alarms.
Digitization plays a crucial role in automotive manufacturing. It equips the interior suppliers with necessary tools and helps them remain flexible and relevant in this modern era. With an increase in customer demand for value-added vehicles, the automotive suppliers are facing an immense pressure in coping up with the changing preferences and requirements, while remaining operational and profitable. Digitization in automotive manufacturing has made companies improve their competitiveness while setting a strong foundation for the future growth in a steadily evolving manufacturing landscape.
+91 9030070085
+91 7801063999
#501C, Bankers Chambers,
A S Raju Nagar, Kukatpally,
Hyderabad Telangana -500 072.